PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
112 C
APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
99.0% min
MOISTURE
|
|
|
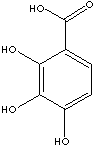
| 2,3,4-TRIHYDROXYBENZOIC ACID | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 610-02-6 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 210-205-9 | |
| FORMULA | (OH)3C6H2COOH | |
| MOL WT. | 170.12 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Pyrogallol-4-carboxylic acid; | |
| ácido 2,3,4-trihidroxibenzoico; Acide 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoïque; Pyrogallolcarboxylic acid; | ||
| DERIVATION |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white to off-white crystalline powder | |
| MELTING POINT | 205 C (Decomposes) | |
| BOILING POINT |
| |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | ||
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
| |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
FLASH POINT |
112 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| There are three isomeric compounds of trihydroxybenzene molecule structure, which all have traditional names respectively. Their names are related with the equivalent dihydroxybenzene compounds. The names of the three compounds indicate which of the hydrogens on the benzene ring portion of the molecule have been replaced by hydroxyl groups. The isomer of 1,2,3-trihydroxybenzene is called pyrogallic acid (or pyrogallol). This compound is a poisonous acid, derived from gallic acid, and used in the manufacturing colorants such as azo dyes and photographic developers and externally as an antimicrobial to treat certain skin diseases. Phloroglucin (or called phloroglucinol) is 1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene which presents as the genin of many glycosides, particulrally in the bark of apple and other trees. It is used in as a reagent for pentoses, pentosans, glycuronates, hydrochloric acid in gastric juice. It is an excellent bone decalcifying agent and a floral preservative. It is used in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals. The 1,2,4- isomer is hydroxyquinol (or called hydroxyhydroquinone). Trihydroxybenzenes have three hydroxyl groups in one benzene ring. They can derive numerous esters and salts. They are used as chemical intermediate to synthesis target molecules of pharmaceuticals, pesticides, stabilizer, antioxidant, colorants, perfumes, photoinitiators, and other organic compounds. Benzoic acid derivatives substituted by hydroxyl group or ether containing oxygen atom have bacteriostatic and fragrant properties. They are typically used in pharmaceutical and perfumery industry. The destructive metabolic property of oxygen containing benzoic acid derivatives such as protocatechuic acid (3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid) and veratric acid (3,4-dimethoxybenzoic acid) is used in the application for pharmaceuticals. Protocatechuic acid is a catabolite of epinephrine. Prazosin, a peripheral vasodilator and antihypertensive, is also an example of the application of veratric acid. Hydroxy and ether substituted benzoic acids feature analogue metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic Acid). They are used as intermediates for pharmaceuticals (especially for antipyetic anlgesic, antirheumatism) and other organic synthesis. They are used as matrix for ionization of peptides, proteins and carbohydrates. 2,3,4-Trihydroxybenzoic acid is the isomer of gallic acid [3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid, C6H2(OH)3COOH] which is obtained from nutgalls and other plants or by the hydrolysis of tannic acid with sulfuric acid. Gallic acid has two functional groups in the same molecule, hydroxyl groups and a carboxylic acid group. They can yield numerous esters and salts including digallic acid which is formed by the reaction of two moles of gallic acid with one another. If gallic acid lose carbon dioxide, pyrogallol is formed. Gallic acid and its derivatives are used in making dyes and inks, photographic developers and has been used as astringents in medically. Some gallates are used as antioxidants in foods. Tannins (tannic acid or gallotannic acid) are esters of digallic acid. They are widely used in tanning leather, dyeing fabrics, manufacturing inks, and in various medical applications (as astringents and to treat some skin diseases). | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white crystalline powder | |
|
ASSAY |
99.0% min |
|
|
MOISTURE |
0.5% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 26-36 | ||
|
|
|